Resources
Search below for resources covering the intersection of climate engagement, social science and data analytics.
RESULTS
What determines the success of movements today?
New research from the Social Change Lab offers key insights into the three main factors that lead to protest wins. First, nonviolent tactics are more likely to lead to successful outcomes relative to violent outcomes—experts consulted were reasonably confident that violence is a less effective approach and the literature supported their view. Second, size of protests is really key, with better-attended protests meaning a higher chance of policy changes and other desired outcomes. Third, favorable sociopolitical context like pre-existing public opinion, the response of the media, whether there are elites (like politicians or celebrities) who support the cause, as well as blind luck are helpful for facilitating successful political outcomes.
Campaign Communications Course
This free course is designed to help grassroots groups to understand the basics of public communications for building a convincing, winning campaign. It can support groups looking for skills on crafting targeted messaging and framing to move people towards social change. You might want to campaign to fight your opponents, convince new audiences, or mobilize audiences that already support your cause. Each of these objectives requires specific communication strategies. The course includes defining public campaigning, communications basics, campaign objectives (neutralizing, informing, persuading and mobilizing), reaching your target group and storytelling. This takes approximately 5 hours to review. Deep dive sections may add 3-4 more hours. Group discussion time may vary.
Innovation Hub
The Innovation Hub is here to empower data learning and strategy among environmental organizations. The Partnership project works directly with data strategists and communications teams at partner organizations to assess common needs and opportunities that can be met with data, and designs original research and experiments, pilot new methods and data tools, and highlight innovative projects. This website share what is being learned through case studies and playbooks, webinars and meetups, newsletters. Workstreams include “extreme weather insights and targeting,” “GOTV and civic engagement,” “membership match resources,” “more insights and data.”
Latino Climate Justice Framework
Climate justice for Latino Americans means centering policies that achieve environmental, energy, and economic justice together. Latino/a/x households pay disproportionately high energy costs, low-income, Latino/a/x households and communities have so far been left behind in the transition to clean energy, and Latino/a/x workers need a pathway to clean energy jobs. Therefore, we need to invest with justice in clean energy, accelerate the transition to renewable energy (i.e., wind, solar, geothermal and small-scale hydropower), and advance economic equity and opportunity for Latino/a/x workers. This resource further details these problems and policy and political solutions, as related to transit, jobs, fossil fuel drilling, climate adaptation, clean water, voting rights, conservation, and more.
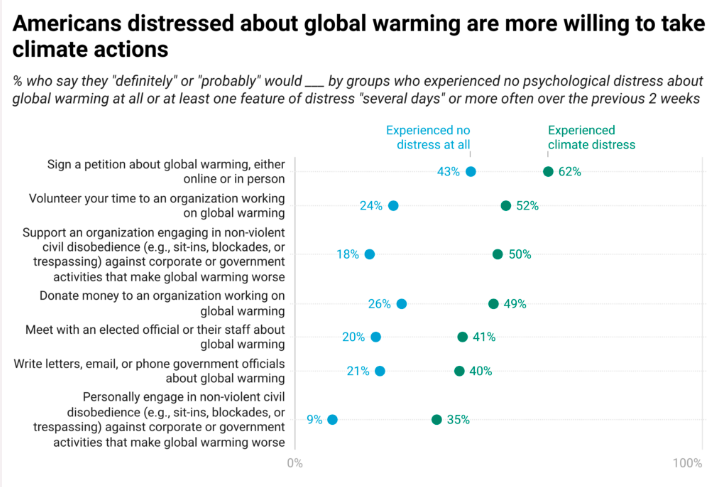
Is distress about climate change associated with climate action?
This report highlights the importance of providing people distressed about climate change with ways to act on their concerns. Americans who had experienced at least one feature of climate distress were much more likely than those who had not to say they had taken different forms of climate action. This includes having signed a petition about global warming (46% vs. 10%, respectively), or having volunteered at an organization working on global warming (19% vs. 2%). Americans who experienced at least one feature of climate distress were more likely than those who had not to say they would meet with an elected official or their staff about global warming (41% vs. 20%, respectively), write letters, email, or phone government officials about global warming (40% vs. 21%), or personally engage in non-violent civil disobedience (e.g., sit-ins, blockades, or trespassing) against corporate or government activities that make global warming worse (35% vs. 9%). Additionally, Americans who reported experiencing at least one feature of climate distress were more likely to say they would join a campaign to convince elected officials to take action to reduce global warming or are already participating in such a campaign, compared to those who reported no distress (56% vs. 19% respectively).
Grassroots Guide: Making Your Activism Accessible
There are some key ways for activists to make their spaces more accessible—to ensure everyone is welcome and encouraged to join movements in whatever way they can. These include: understanding the right choice of location for events/actions; meeting attendee needs; creating space for every identity; employ proper pandemic safety measures. For virtual events and meetings, consider preparation before the meeting and use specific in-meeting tactics. Regarding communications, use clear language and modes of communication that all potential audiences can understand. Write image descriptions. Also, be sure to foster a group culture dedicated to accessibility.
Grassroots Guide: Navigating Turnover In Activist Groups
There are some key strategies that grassroots groups can employ to avoid dissolving. These are especially helpful for student-run groups, which can struggle to pass along the group's resources and knowledge to the next generation of student organizers, as many lack a permanence of structure. These strategies include: support and guide new members via training and upskilling; build institutional memory; create a blueprint for group operations; have strong onboarding and outboarding processes; institutionalize involvement; engage with the student association/body; get teachers to support your campaign(s); outline institutions in your school; get support from staff unions; and create solidarity with staff causes. This report describes these strategies in detail. Some specific challenges by student groups have included: divestment organizers were concerned about groups who won and didn’t know where to go from there; groups have been struggling to navigate online organizing; there are ongoing concerns related to general turnover and capacity when students graduate (particularly those who have been members of a group for a while; a lack of support from former members leads to more energy and time needed to restart after a high rate of turnover; anger towards the school administration leads to forgetting about turnover periods, thus the workload for the next semester is larger.
The “Before Action Review” is a series of questions for a team to answer together to improve their collective project. The five questions are: What is our intended result? What are our success measures? What challenges will we face? What did we learn from last time? What do we think will make us successful this time? The “After Action Review” is a similar set of questions to digest together, as a team, after a project attempt: What is our intended result? What were our actual results? What caused our results? What lessons should we take forward for next time? These kinds of collective planning and processing create the conditions for people to develop their: knowledge — information or understanding gained from experience or education; skills — the ability to do something that comes from training, experience, or practice; and wisdom — the ability to contemplate and act using knowledge, experience, understanding, common sense and insight.
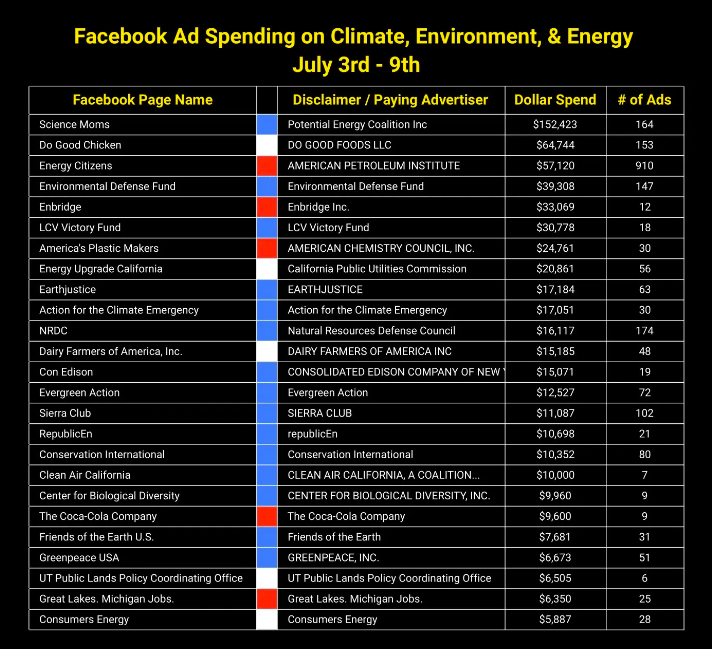
Climate groups use “climate anxiety” to spur grassroots action
Various climate groups have recently used messages invoking “climate anxiety” to spur grassroots action. Science Moms and Action for the Climate Emergency have joined the Environmental Defense Fund and Climate Emergency Fund in running Facebook and Instagram ads about climate anxiety in recent weeks. A group called RepublicEn has been running Meta ads using conservative messengers like evangelicals, military figures, and elected officials to create a permission structure for Republican voters to support climate action. The dominant narrative about climate change or energy on social media last week concerned a report showing that some of the U.S. Strategic Petroleum Reserve was shipped to countries like China. Pages like Breitbart and Tucker Carlson seized on the news to accuse the Biden administration of “treason”, but their content went mostly unchecked by progressive pages.
Building long-lasting grassroots power requires centering concrete issues and the humanity of individuals you’re organizing. Many organizations in West Virginia are cultivating organizers, building organizations that can sustainably organize local communities according to their needs for years to come, incorporating mutual aid, and more, in an effort to win and wield political power. In this article, The Forge contributor Mat Hanson discussed organizational strategies with multiple people involved in grassroots power building in West Virginia: Katey Lauer, co-chair of West Virginia Can’t Wait; Nicole McCormick, a founding member of the West Virginia United caucus and rank-and-file leader in the successful teacher’s strike; Dr. Shanequa Smith of Restorative Actions and the Black Voters Impact Initiative; and Joe Solomon, the co-founder and co-director of Solutions Oriented Addiction Response (SOAR), a volunteer-based organization that advocates for harm-reduction strategies to the opioid crisis.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page